All About Pacific Cod & Black Cod
"The Cods": Pacific Cod & Black Cod
“Cod” is the common (and confusing) name perhaps most intended to refer to demersal fish in the genus Gadus. This includes the two main species, Atlantic cod, which lives in the colder waters and deeper seas of the North Atlantic, and Pacific cod, found spanning the eastern and western regions of the northern Pacific. However, some demersal Gadus members (like Alaska pollock) go by other names, while at the same time “cod” has come to serve as a vernacular term to blanket a number of regional fish species, like Anoplopoma fimbria, or “Black Cod.”
Product Info
Alaska (Pacific) Cod
- Caught: Throughout the year
- Location: Aleutian Islands (Western Gulf / Bering Sea)
- Method: Pot caught and Longline
- Vacuum-packed & flash frozen in 6-8 oz portions
- 10 lb box dimensions: 15” x 10 ¼” x 6½”
- Generally holds up to 18 months
Black Cod (aka Sablefish)
- Caught: mid March- early November
- Location: SE Alaska
- Method: Longline (hook and line)
- Vacuum-packed & flash frozen in 6-8 oz portions
- 5 lb box dimensions: 12” x 10 ⅜” x 4 ⅝”
- 10 lb box dimensions: 15” x 10 ¼” x 6½”
- Generally holds up to 2 years
All About Pacific Cod
Gadus macrocephalus is a transoceanic species of ray-finned “true cod,” found across the continental shelf and upper slopes, ranging from the Yellow Sea to the Bering Strait, along the Aleutian Islands, to as far south as Los Angeles. Pacific Cod have three separate dorsal fins and catlike whiskers on their bottom jaw. They can grow to be up to 50 inches in length, 50 pounds in weight, and up to eighteen years of age. Pacific Cod take to large schools in depths of about 3,000 feet, reaching their peak spawning period in March. Females lay a large number of slightly adhesive eggs that sink to the the bottom, fortunate to land in a safe place for development.
Alaska Select’s Pacific Cod
Pacific Cod has become a significant source for commercial fishing and is also known as gray cod or grey cod, and grayfish or greyfish. Different fisheries use different techniques, such as:
- Hook and line fishing (The National Marine Fisheries Service often prohibits directed fishing for Pacific cod by catcher/processors using hook-and-line gear in the Gulf of Alaska)
- Bottom trawls (a widely-deemed problematic method), and
- Pots (certified by the Marine Stewardship Council to be sustainable in the Aleutian Islands, where Alaska Select sources its Pacific Cod)
In all cases, the species is managed through quotas, or regulated catch shares/permitted allotments. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association deems U.S. wild-caught Pacific Cod “a smart seafood choice because it is sustainably managed and responsibly harvested under U.S. regulations.” Alaska’s trends are considered stable after increasing rapidly in the late 70’s and early 80’s.
Nutritional Value of Pacific Cod
Pacific cod is such significant source of vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids that Cod livers are specifically processed into cod liver oil--a sought out supplement. Pacific Cod is also high in amino acids and selenium.
- Omega-3 fatty acids provide cardiovascular benefits such as preventing erratic heart rhythms, aiding blood flow inside arteries where clots can cause heart attacks, and balancing the ratio of good High Density Lipoprotein (also preventing atherosclerosis). Omega-3s reduce triglycerides, a potentially harmful fat in our bloodstream. Omega-3s also reduce inflammation, which is a key component in the processes that turns cholesterol into artery-clogging plaques.
- Vitamin A is the umbrella term for several fat-soluble compounds. These compounds are vital to many processes in the body, such as the maintenance of healthy vision, immune system functions, organ upkeep, and growth and development during pregnancy.
- Vitamin D is essential in regulating the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, facilitating normal immune system functions and the healthy development of bones and teeth. Vitamin D helps with weight-loss and depression prevention.
- Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant, promoting healthy skin, heart, and immune system, and positively affecting vision and symptoms of arthritis.
- Amino acids are the building blocks of protein, needed for the development of tissues in the body, including muscles. They are the precursors to hormones, immune response, repair, and other molecular essentials for health.
- Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant, supporting liver function, in turn detoxifying and clearing potentially harmful compounds such as pesticides, drugs, and heavy metals from the body. Selenium reduces risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and cancer, combating premature aging and risk of stroke.
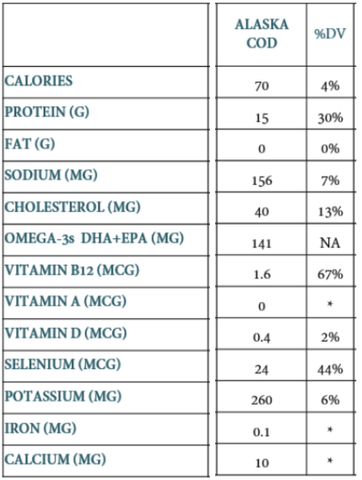
Up-to-date nutritional value of Alaskan Cod (2019), based on a 3 oz (⅔ cup, or 85g) serving serving size:
Culinary Profile of Pacific/Alaska Cod
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) places Alaskan Cod on their “Top 10 Fish Favorites” list, complimenting its mild flavor. Combined with a dense, flaky, white flesh, the approachable qualities make it a popular choice beyond general seafood lovers. Cod is popular in fish sticks, on sandwiches, and as meal centerpieces, easily complimented by a full spectrum of spices. Fillets are commonly prepared simply by baking, grilling, sautéing, steaming, broiling, or deep-frying. Searing fillets (dressed in a favorite rub, or spice coating) before grilling or baking can create a crisp, flavorful outer layer. Breading the fillets or wrapping them in tinfoil can help retain moisture as well.
Check out our cod recipes.
All About Black Cod (aka Sablefish)
Anoplopoma fimbria, or "sablefish," is native to the North Pacific and is the only specie of fish in the genus Anoplopoma. It’s perhaps for this reason, to associate it with the familiar, that it has taken on the region-inspired nicknames, most commonly, “Black Cod.” Adult sablefish are opportunistic predators, feeding on Pacific cod, Alaskan pollock, eulachon, herring, squid, euphausiids, and jellyfish. They have been reported to live for up to 94 years, although the majority of the commercial catch are on average 20 years old (old enough to have spawned). Sablefish are found in the northeastern Pacific Ocean from northern Mexico all the way up to the Gulf of Alaska, west to the Aleutian Islands and up into the Bering Sea. The northern population inhabits Alaska and northern British Columbia waters.
Alaska Select’s Black Cod
While the southern population of Pacific Coast sablefish are “near” target population levels, Alaska sablefish, specifically, are above target population levels, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA). The current fishing rates are considered to promote population growth. The fishing season runs from approximately March to November, with trawl gear (a more controversial method) harvesting ten percent of the annual quota, and “fixed” longlines and pots (considered the least impactful) harvesting 90 percent of the annual quota. Alaska Select sources its Black Cod from set pots in the Aleutian Islands, and specifically buys 45 pound fish for the health of the fish, the taste and the texture.
Nutritional Value of Black Cod
Sablefish is so high in omega-3s, it actually contains more than wild salmon. It’s also high in vitamin B-12, niacin, selenium, iodine, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, zinc and calcium.
- Omega-3 fatty acids provide cardiovascular benefits such as preventing erratic heart rhythms, aiding blood flow inside arteries where clots can cause heart attacks, and balancing the ratio of good High Density Lipoprotein (also preventing atherosclerosis). Omega-3s reduce triglycerides, a potentially harmful fat in our bloodstream. Omega-3s also reduce inflammation, which is a key component in the processes that turns cholesterol into artery-clogging plaques.
- Vitamin B12 helps lower levels of homocysteine, reducing damage to artery walls.
- Niacin (Vitamin B-3) is essential to the entire body’s functioning. Niacin can help lower cholesterol, ease and even prevent arthritis, and boost brain function.
- Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant, supporting liver function, in turn detoxifying and clearing potentially harmful compounds such as pesticides, drugs, and heavy metals from the body. Selenium reduces risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and cancer, combating premature aging and risk of stroke.
- Iodine is a mineral needed for proper thyroid functions, which affect metabolism, bone health, immune response, and development of the central nervous system.
- Phosphorus is a mineral contributing to the build of strong bones and teeth. It also aids in healthy metabolism, or the convergence of food to energy.
- Magnesium lessens improves the flow of blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body, resulting in the overall increased health of many systems.
- Zinc is a trace element necessary for a healthy immune system--a zinc deficiency can cause susceptibility to disease and illness.
- Iron is an essential mineral for the protein hemoglobin to transport oxygen throughout the bloodstream.
- Calcium is largely responsible for the development and maintenance of strong bones, as well as heart, muscle, and nerve functions.
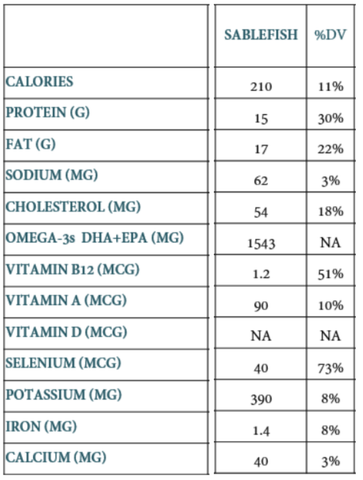
Up-to-date nutritional value of Black Cod (2019), based on a 3 oz (⅔ cup, or 85g) serving serving size:
Culinary Profile of Black Cod
Sablefish is considered a delicacy in countries throughout the world--reputed for its rich, yet mild flavor, soft-texture, and high oil content. The meat is referred to as “velvety” or “satiny,” hence its common market nickname, “Butterfish.” The flesh parts into large, white, delicate flakes that absorb marinades well. Its high fat content makes fillets good for grilling, smoking, frying, or served as sushi.
Sablefish is commonly served as a meal centerpiece, pairing with a full spectrum of sauces, potatoes, rice dishes, and vegetables. It is popular on salads and specialty sandwiches.
Check out our cod recipes.


